Designed by
Evgeny Zolin
Under construction! |
Complexity of Modal Logics
The syntax for formulas of the modal logic K:
⊥
| p
| ¬φ
| φ ∧ ψ
| φ ∨ ψ
| φ → ψ
| 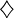 φ
| φ
| 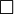 φ φ
|
|
Check for the
latest updates
Under construction! |
| Complexity of reasoning problems |
| Problem |
Complexity |
Comments and references |
| Local satisfiability
|
|
|
| Global satisfiability
|
|
|
| Global consequence
|
|
|
| Important properties of the logic
|
| Finite model property
|
|
|
| Tree model property
|
|
|
Definitions
Let L be a logic (i.e. a language + a class of frames).
A (finite) set of formulae Γ is usually called a modal theory.
L-frame is a Kripke frame where L is valid:
F 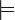 L.
L.
L-model is a Kripke model based on an L-frame.
- Local satisfiability.
A formula φ is locally L-satisfiable
if there exists a L-model M and its world x
such that M,x 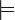 φ.
φ.
Usually, one considers a dual notion: a formula φ is L-valid
if it is valid in all L-frames.
Clealy, φ is L-valid iff
¬φ is not L-satisfiable.
- Global satisfiability.
A formula φ is globally L-satisfiable
if there exists an L-model M
such that M 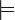 φ.
φ.
A modal theory Γ is L-consistent
if all its formulae are globally L-satisfiable (all in a single model).
- Global consequence relation.
A formula φ is a global consequence
of a theory Γ in the logic L if,
for every L-model M,
if M 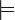 Γ
then M
Γ
then M 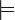 φ.
φ.
Instead of a finite theory Γ, we can deal with a single formula ψ
(by taking the conjunction of all formulae in Γ).
Notation:
-
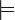 L φ
— a formula φ is L-valid,
L φ
— a formula φ is L-valid,
- Γ
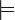 L ⊥
— a modal theory Γ is L-inconsistent,
L ⊥
— a modal theory Γ is L-inconsistent,
- Γ
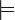 L φ
— a formula φ is a global consequence of a theory Γ in L.
L φ
— a formula φ is a global consequence of a theory Γ in L.
Clearly, the first two are special cases of the third.
When estimating complexity, it is convenient to deal with the negation
of these problems (because it is usually the negations that are in NP, NExpTime etc,
whereas the original problems are in co-NP, co-NExpTime etc).
In Description Logic, the 2nd and 3rd problems are equivalent
(modulo introducing a new role). In uni-modal logic (or in a logic with a fixed set of modalities),
this reduction does not work, since
we have no extra modality.
This distinction is crucial: in S4, the 2nd problem is NP-complete,
whereas the 1st and 3rd are PSpace-complete (so the 3rd is not reducible to the 2nd problem, unless NP=PSpace).
References
Books
- Handbook of Modal Logic —
Patrick Blackburn,
Johan van Benthem,
Frank Wolter (editors).
Studies in Logic and Practical Reasoning, Volume 3,
Elsevier, 2007.
ISBN 0-444-51690-5
- Modal Logic —
Patrick Blackburn,
Maarten de Rijke,
and
Yde Venema.
Cambridge Tracts in Theoretical Computer Science, Volume 53,
Cambridge University Press, 2001. ISBN 0-521-52714-7
- Modal Logic —
Alexander
Chagrov and
Michael Zakharyaschev.
Oxford Logic Guides, Volume 35, Oxford University Press, 1997.
ISBN 0-19-853779-4
- Computational Complexity —
Christos H. Papadimitriou.
Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, 1994. ISBN 0-201-53082-1.
Theses on complexity of ordinary Modal Logics
- Complexity of modal logics.
Edith Spaan
(now Edith Hemaspaandra).
PhD Thesis, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science,
University of Amsterdam, 1993.
Advised by Johan van Benthem.
- Komplexität modaler Logiken
(Complexity of Modal Logics)
[ pdf ]
Thomas Schneider.
Diplomarbeit, Friedrich-Schiller-Universitat Jena, 2002, 65 pages. (in German)
- The complexity of decision problems for modal propositional logics.
C.C. Chen.
PhD Thesis, Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering,
National Taiwan University. Taipei, Taiwan, 1993.
- Сложность пропозициональных логик с конечным числом переменных
(Complexity of propositional logics with a finite number of variables)
М.Н.Рыбаков (M.N.Rybakov).
PhD Thesis, 2005. (in Russian)
See abstract here.
Papers on complexity of ordinary Modal Logics
- On the complexity of fragments of modal logics.
[ pdf ]
Linh Anh Nguyen.
Advances in Modal Logic, vol. 5, , pp. 249–268, 2005.
- Complexity of Simple Dependent Bimodal Logics.
[ pdf ]
Stéphane Demri.
Tableaux 2000,
LNCS
(LNAI),
vol. 1847, pp. 190–204, 2000.
- The complexity of propositional modal theories and
the complexity of consistency of propositional modal theories.
[ pdf ]
Cheng-Chia Chen and
I-Peng Lin.
Logical Foundations of Computer Science (LFCS'94),
LNCS,
vol. 813, pp. 69–80. Springer, Berlin, 1994.
- A guide to completeness and complexity for modal logics of knowledge and belief.
[ pdf ]
Joseph Y. Halpern,
Yoram Moses.
Artificial Intelligence, vol. 54, pp. 319–379, 1992.
- The computational complexity of provability in systems of modal logic.
[ pdf ]
R.E.Ladner.
SIAM Journal of Computing,
vol. 6, num. 3, pp. 467–480, 1977.
"Graded Modalities" series of papers
- Graded Modalities VII: The modality of finite.
[ pdf ]
Uliano P. Balestrini
and
Maurizio Fattorosi-Barnaba.
Mathematical Logic Quarterly, vol. 45, pp. 471–480, 1999.
- Graded Modalities VI: An infinitary graded modal logic.
[ pdf ]
Maurizio Fattorosi-Barnaba
and
Silvano Grassotti.
Mathematical Logic Quarterly, vol. 41, pp. 547–563, 1995.
- Graded Modalities V: Decidability by filtration for graded normal logics.
[ pdf ]
Claudio Cerrato.
Studia Logica, vol. 53, pp. 61–74, 1994.
Note: this paper contains a serious error;
thus it does not prove decidability of transitive graded modal logics.
A counterexample to the proof is given in "How many legs do I have" (below).
A correct proof is given in "A note on the complexity of the satisfiability problem for graded modal logics" (below).
- Graded Modalities IV: General canonical models for graded normal logics.
[ pdf ]
Claudio Cerrato.
Studia Logica, vol. 49, pp. 241–252, 1990.
- Graded Modalities III: The completeness and compactness of S40.
[ pdf ]
Maurizio Fattorosi-Barnaba
and
Claudio Cerrato.
Studia Logica, vol. 47, pp. 99–110, 1988.
- Graded Modalities II: Canonical models.
[ pdf ]
Francesco de Caro.
Studia Logica, vol. 47, pp. 1–10, 1988.
- Graded Modalities I.
[ pdf ]
Maurizio Fattorosi-Barnaba
and
Francesco de Caro.
Studia Logica, vol. 44, pp. 197–221, 1985.
Other papers on Graded Modal Logics and related logics
- Modal Logics with Counting.
[ pdf ]
Carlos Areces, Guillaume Hoffmann and Alexandre Denis.
Proc. of Logic, Language, Information and Computation.
17th International Workshop, WoLLIC 2010, Brasilia, Brazil, July 6-9, 2010.
LNCS vol. 6188, pp. 98-109, Springer, 2010.
- Goldblatt-Thomason-style theorems for graded modal language.
[ pdf ] (from here)
Katsuhiko Sano and Minghui Ma.
In
Lev Beklemishev,
Valentin Goranko
and Valentin Shehtman, editors,
Proc. of AiML 2010,
College Publications, 2010,
pp. 330–349.
- Terminating tableaux for SOQ with number restrictions on transitive roles.
[ pdf ] (from here)
Mark Kaminski and
Gert Smolka.
In Proc. of DL 2009,
CEUR vol. 477, Oxford, UK, July 27–30, 2009.
- Terminating tableaux for graded hybrid logic with global modalities and role hierarchies.
[ pdf ]
(from here)
Mark Kaminski,
Sigurd Schneider, and
Gert Smolka.
In TABLEAUX 2009,
LNCS
(LNAI),
vol. 5607, pp. 235–249, Springer, 2009.
- A note on the complexity of the satisfiability problem for graded modal logics.
[ pdf ]
Yevgeny Kazakov,
Ian Pratt-Hartmann.
In Proc. of LICS 2009,
pp. 407–416, IEEE Computer Society, 2009.
• Technical Report, arXiv:0905.3108v1, 2009.
[ pdf ]
- How many toes do I have? Parthood and number restrictions in description logics.
[ pdf ]
Lutz Schröder
and
Dirk Pattinson.
In Gerhard Brewka, Jerôme Lang (eds.),
Proc. of KR 2008,
pp. 307–218,
AAAI Press, 2008.
- How many legs do I have? Non-simple roles in number restrictions revisited.
[ pdf ]
Yevgeny Kazakov,
Ulrike Sattler, and
Evgeny Zolin.
In N.Dershowitz, A.Voronkov (eds),
Proc. of LPAR 2007,
LNCS, vol. 4790,
pp. 303–317, Springer, 2007.
• Technical Report: Is your RBox safe?
[ pdf ]
- A tableau method for graded intersections of modalities: A case for concept languages.
[ pdf ]
Ani Nenkova.
Journal of Logic, Language, and Information,
vol. 11, num. 1, pp. 67–77, Springer, 2002.
- PSpace reasoning for graded modal logics.
[ pdf ]
(from here)
Stephan Tobies.
Journal of Logic and Computation, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 85–106, 2001.
This is a significantly extended and improved version of an earlier paper:
A PSpace algorithm for graded modal logic.
[ pdf ]
Stephan Tobies.
In H.Ganzinger (ed),
Proc. of CADE-16,
LNCS
(LNAI),
vol. 1632, pp. 52–66, Springer-Verlag, 1999.
- A note on graded modal logic.
[ TEX.pdf | PS.pdf | SCAN.pdf ]
Maarten de Rijke.
Studia Logica, vol. 64, pp. 271–283, 2000.
Note: TEX.pdf is in modern notation and with some corrections of proofs.
- PSpace reasoning for DLs with qualifying number restrictions
[ pdf ]
Stephan Tobies.
Technical Report: LTCS-99-11. 1999.
- A set-theoretic approach to automated deduction in graded modal logics.
[ pdf ]
Angelo Montanari
and
Alberto Policriti.
In Proc. of IJCAI'97,
pp. 196–201, Morgan Kaufmann, 1997.
- Translating graded modalities into predicate logic.
[ pdf ]
Hans Jürgen Ohlbach,
Renate A. Schmidt, and
Ullrich Hustadt.
In H.Wansing (ed.),
Proof Theory of Modal Logic.
Applied Logic Series, vol. 2, pp. 253–291.
Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1996.
• Technical Report MPI-I-95-2-008, Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik,
Saarbruken, Germany, 1995. Extended abstract:
[ pdf ]
- Symbolic arithmetical reasoning with qualified number restrictions.
[ pdf ]
Hans Jürgen Ohlbach,
Renate A. Schmidt, and
Ullrich Hustadt.
In Proc. of International Workshop on Description Logics'95 (DL'95),
pp. 89–94, 1995.
- Counting objects.
[ pdf ]
Wiebe van der Hoek
and
Maarten de Rijke.
Journal of Logic and Computation, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 325–345, 1995.
- Graded modalities in epistemic logic.
[ pdf ]
Wiebe van der Hoek
and
John-Jules Ch. Meyer.
In A.Nerode and M.Taitslin (eds),
Logical Foundations of Computer Science (LFCS'92),
LNCS,
vol. 620, pp. 503–514. Springer, Berlin, 1992.
• Technical Report, 1993:
[ pdf ]
- On the semantics of graded modalities.
Wiebe van der Hoek.
Journal of Applied Non-Classical Logics,
vol. 2, num.1, pp. 81–123, 1992.
Under the same title, there were also:
• Technical Report IR-246, Free University of Amsterdam, 1991.
• Chapter 4 in his PhD Thesis: Modalities for Reasoning about Knowledge and Quantities,
Free University of Amsterdam, 1992.
[ TEX.pdf | SCAN.pdf ]
Note: TEX.pdf is in modern notation, with simplified proofs and numerous corrections, but no figures.
- Normal predicative logics with graded modalities.
[ pdf ]
Francesco de Caro.
Studia Logica, vol. 47, num. 1, pp. 11–22, 1988.
- In so many possible worlds.
[ TEX.pdf | SCAN.pdf ]
Kit Fine.
Notre Dame Journal of Formal Logic,
vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 516–520, 1972.
Note: TEX.pdf is in moder notation and with corrections in proofs.
- Grades of modality.
L.F.Goble.
Logique et Analyse, vol. 13, pp. 323–334, 1970.
Papers on applications of Graded Modal Logics and related topics
- Graded-CTL: Satisfiability and Symbolic Model Checking.
[ pdf ]
Alessandro Ferrante, Margherita Napoli and Mimmo Parente.
Formal Methods and Software Engineering.
11th International Conference on Formal Engineering Methods ICFEM 2009, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, December 9-12, 2009. Proceedings.
LNCS vol. 5885, pp. 306-325, Springer, 2009.
- CTL Model-Checking with Graded Quantifiers.
[ pdf ]
Alessandro Ferrante, Margherita Napoli and Mimmo Parente.
Automated Technology for Verification and Analysis.
6th International Symposium, ATVA 2008, Seoul, Korea, October 20-23, 2008. Proceedings
LNCS vol. 5311, pp. 18-32,
Springer, 2008.
- Strong Completeness of Coalgebraic Modal Logics.
[ pdf ]
Lutz Schröder
and
Dirk Pattinson.
In Susanne Albers, Jean-Yves Marion (Eds.),
Proc. of STACS 2009,
pp. 673-684.
- PSpace bounds for rank 1 modal logics.
[ pdf ]
Lutz Schröder
and
Dirk Pattinson.
In ACM Transactions on Computational Logic,
vol. 10, issue 2, pp. 1–33, 2009.
Previous version of the paper:
• In Rajeev Alur (ed.),
Proc. of LICS 2006,
pp. 231–242.
IEEE, 2006.
[ pdf ]
•
Technical Report, 2006:
[ pdf ]
- Generalizing the Goldblatt-Thomason Theorem and Modal Definability.
[ pdf ]
Suvi Lehtinen.
Academic Dissertation,
University of Tampere, 2008.
- A finite model construction for coalgebraic modal logic.
[ pdf ]
Lutz Schröder.
Journal of Logic and Algebraic Programming,
vol. 73, pp. 97-110, Elsevier Science, 2008.
This is an extended version of an earlier paper with the same title:
• In L.Aceto and A.Ingólfsdóttir (eds.),
Proc. of FOSSACS 2006,
LNCS,
vol. 3921, pp. 157–171, Springer, 2006.
[ pdf ]
- Beyond rank 1: Algebraic semantics and finite models for coalgebraic logics.
[ pdf ]
Lutz Schröder
and
Dirk Pattinson.
In Roberto Amadio (ed.),
Proc. of FOSSACS 2008,
LNCS,
vol. 4962, pp. 66–80, Springer, 2008.
- Rank-1 modal logics are coalgebraic.
[ pdf ]
Lutz Schröder
and
Dirk Pattinson.
In Wolfgang Thomas, Pascal Weil (eds.),
Proc. of STACS 2007,
LNCS,
vol. 4393, pp. 573–585, Springer, 2007.
- Possibility based modal semantics for graded modifiers.
[ pdf ]
Jorma K. Mattila.
In P. Melin et al. (eds.),
Proc. of IFSA 2007,
LNCS
(LNAI),
vol. 4529, pp. 220–230, Springer, 2007.
- Graded modal operators and fixed points (in Russian).
[ pdf | typos ]
Sergey Mardaev.
Vestnik NGU (Bulletin of the Novosibirsk State University),
Mathematics series, vol. 6, num. 1, pp. 70–76, 2006.
- Presburger modal logic is PSpace-complete.
[ pdf ]
Stéphane Demri
and
Denis Lugiez.
In
Proc. of
IJCAR 2006,
LNCS,
vol. 4130, pp. 541–556, Springer, 2006.
- Modifier logics based on graded modalities.
[ pdf (excerpt) ]
Jorma K. Mattila.
Journal of Advanced Computational Intelligence and Intelligent Informatics
(JACIII),
vol. 7, num. 2, pp. 72–78, Fuji Technology Press, 2003.
- Graded modalities and resource bisimulation.
[ pdf ]
Flavio Corradini,
Rocco De Nicola, and
Anna Labella.
In C. Pandu Rangan, V. Raman, R. Ramanujam (eds.),
Proc. of FSTTCS 1999,
LNCS, vol. 1738, pp. 381–393,
Springer, 1999.
This page is developed permanently.
Comments are welcome by
E-mail:
EZolin (at) cs.man.ac.uk
|
| © Powered by Evgeny Zolin
|
 φ
|
φ
|  φ
φ

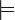 L.
L.
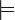 φ.
φ.
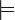 φ.
φ.
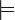 Γ
then M
Γ
then M 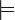 φ.
φ.
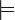 L φ
— a formula φ is L-valid,
L φ
— a formula φ is L-valid,
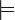 L ⊥
— a modal theory Γ is L-inconsistent,
L ⊥
— a modal theory Γ is L-inconsistent,
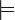 L φ
— a formula φ is a global consequence of a theory Γ in L.
L φ
— a formula φ is a global consequence of a theory Γ in L.