


Next: Axioms
Up: OIL-Lite
Previous: Concrete type expressions
A slot-constraint consists of a slot name
 followed by one or more constraints that apply to the slot,
written
followed by one or more constraints that apply to the slot,
written
![$ \ensuremath{\textsf{\textsl{SN}}}[a_1,\ldots,a_n]$](img44.png) . Each constraint can be either:
. Each constraint can be either:
- A value constraint with either a list of one or more
class-expressions or a list of one or more
concrete type expressions, written
 .
.
- A value-type constraint with either a list of one or more
class-expressions or a list of one or more
concrete type expressions, written
 .
.
- A has-filler constraint with either a list of one or more
individual names or a list of one or more data values,
written
 .
.
- A max-cardinality constraint with a non-negative integer
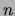 followed (optionally) by either a class expression
followed (optionally) by either a class expression 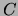 or a
concrete-type-expression, written
or a
concrete-type-expression, written 
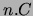 (
(
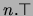 if the expression is omitted).
if the expression is omitted).
- A min-cardinality constraint with a non-negative integer
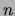 followed (optionally) by either a class expression or a concrete
type expression, written
followed (optionally) by either a class expression or a concrete
type expression, written 
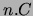 (
(
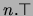 if the expression is omitted).
if the expression is omitted).
- A cardinality constraint with a non-negative integer
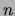 followed (optionally) by either a class expression
followed (optionally) by either a class expression 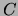 or a concrete
type expression, written
or a concrete
type expression, written 
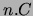 (
(
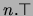 if the class
expression is omitted).
if the class
expression is omitted).
In order to maintain the decidability of the language, cardinality
constraints can only be applied to simple slots. A
simple slot is one that is neither transitive nor has any transitive
subslots. However, as the transitivity of a slot can be inferred (e.g.,
from the fact that the inverse of the slot is a transitive slot),
simple slot is defined in terms of the translation into
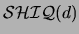 : a slot
: a slot
 in an ontology
in an ontology
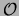 is a simple slot iff
is a simple slot iff
 is a simple role in the
is a simple role in the
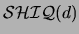 terminology
terminology
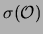 .
.



Next: Axioms
Up: OIL-Lite
Previous: Concrete type expressions
Ian Horrocks
2000-09-10
![]() followed by one or more constraints that apply to the slot,
written
followed by one or more constraints that apply to the slot,
written
![]() . Each constraint can be either:
. Each constraint can be either:
![]() : a slot
: a slot
![]() in an ontology
in an ontology
![]() is a simple slot iff
is a simple slot iff
![]() is a simple role in the
is a simple role in the
![]() terminology
terminology
![]() .
.